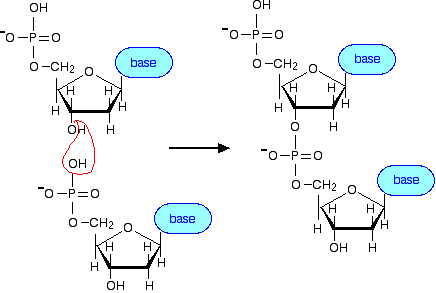
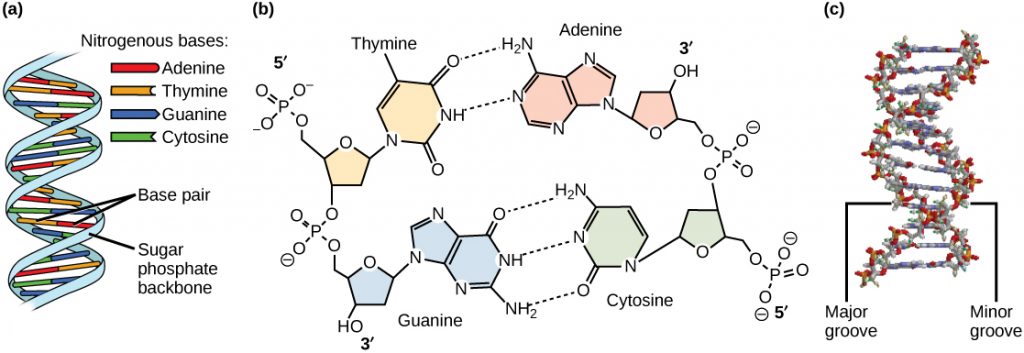
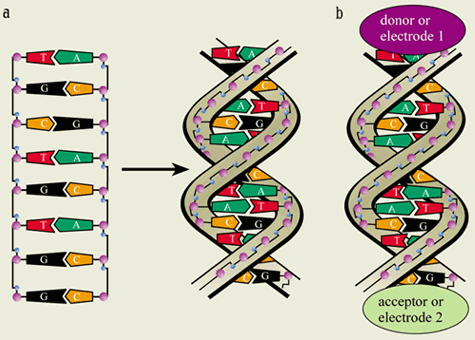
DNA is known as a double helix because there are two intertwined strands within each molecule of DNA In the image above, a corkscrew is shown on the left, with the helical region labeled The image in the center shows the structure of DNA Note that there are two strands one shown in blue, one · Filling duplexes I and III with BrdUTP (resulting in IBr and IIIBr, Figure 1C) yields an internally double labeled DNA molecule containing two BrdU residues separated by 3 bp In principle, the same or different classIIS REases, producing 5' protruding 4nt cohesive ends, could be used for the cleavage of PCR1 and PCR2Iii The human genome is distributed in 23 pairs of
The Structure Of Dna
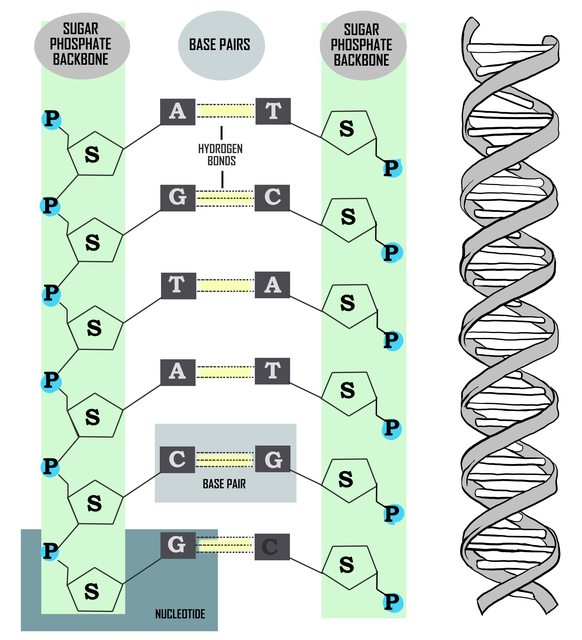
Double stranded dna molecule labeled
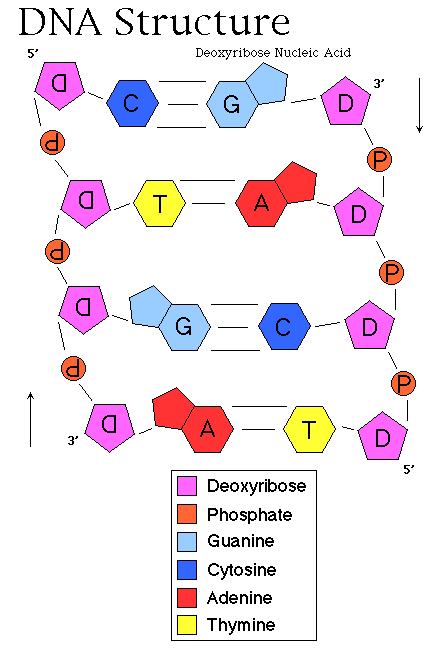
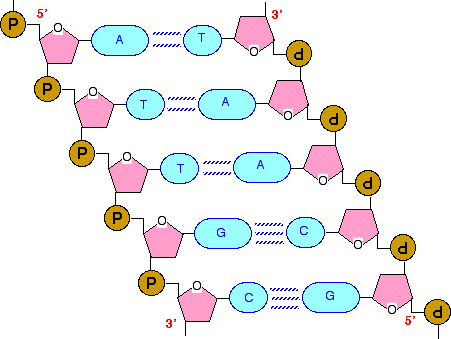
Double stranded dna molecule labeled-The backbone of DNA is based on a repeated pattern of a sugar group and a phosphate group The full name of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, gives you the name of the sugar present deoxyribose Deoxyribose is a modified form of another sugar called ribose I'm going to give you the structure of that first, because you will need it later anyway98 · Our labeling procedure was based on the ligation of two short dsDNA fragment (732 bp) containing labeled nucleotides at multiple positions to the ends of the DNA molecule These fragments were obtained in the following way




Dna Sammisbiologyblog
Two nitroxide spin labels 4amino2,2,6,6tetramethylpiperidine1oxyl were attached at the two ends of the molecules Singlestranded DNAs and doublestranded DNAs (DNA duplexes) in frozen at 77 K glassy water / glycerol solutions were studied using pulsed electron–electron double resonance (PELDOR)The DNA of E coli appears to consist of a single, enormous doublestranded DNA molecule with a molecular weight of about 28 x 10 9, a thickness of about nm and a contour length of about 1,360µm E coli DNA contains 4 million deoxyribonucleotide pairs This DNA is a closed and unfolded circle Due to interaction with nucleoid proteins and RNA, the circular DNA folds into aDeoxyribose Opposite strands of DNA are_____ to each other antiparallel Table 122 Three samples of DNA contain the
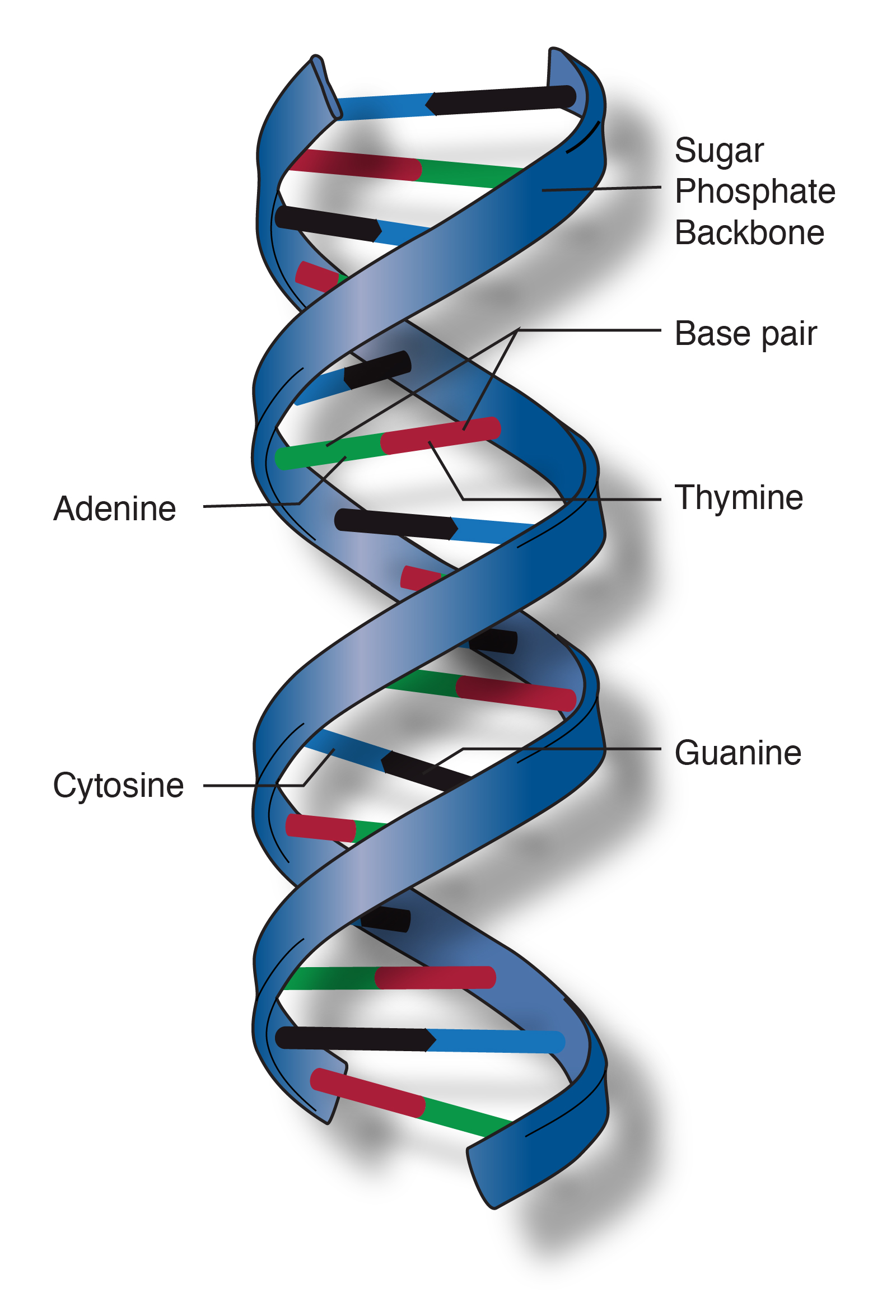
Double helix is the description of the structure of a DNA molecule A DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder Each strand has a backbone made of alternating groups of sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groupsA helix is a winding structure like a corkscrew;The doublehelix model of DNA structure was first published in the journal Nature by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, (X,Y,Z coordinates in 1954) based on the work of Rosalind Franklin and her student Raymond Gosling, who took the crucial Xray diffraction image of DNA labeled as "Photo 51", and Maurice Wilkins, Alexander Stokes, and Herbert Wilson, and base
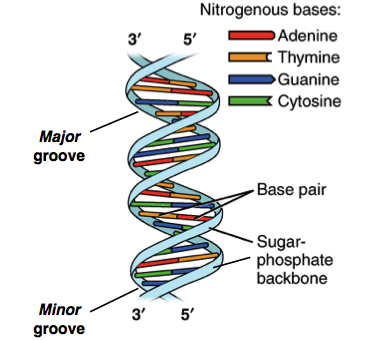
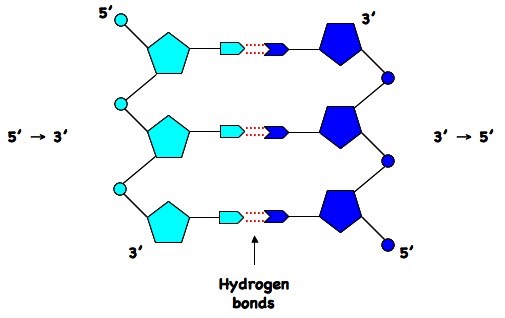
The structures in the diagram labeled W are ?A doublestranded DNA molecule contains a total of 1 purines and 1 pyrimidines This DNA molecule could be composed of _____ 1 thymine and 1 adenine molecules If one strand of a DNA molecule has the sequence of bases 5'ATTGCA3', the other complementary strand would have the sequence _____ 5'TGCAAT3' What is the structural feature that allows DNA toThe DNA molecule actually consists of two such chains that spiral around an imaginary axis to form a double helix (spiral) Nucleic acid molecules are incredibly complex, containing the code that guarantees the accurate ordering of the amino acids in all proteins made by living cells




Nucleic Acid Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Britannica



4 Dna Protein Production National 5 Biology
Transcribed image text A) The diagram below represents an untwisted, doublestranded DNA molecule 5 pts Label each sugar group on the diagram with a letter S 2 Label each phosphate group with a letter P 3A, T, C and G have already been labeled Match and label the rest of the nitrogenous bases 4DNA Molecule Two Views Legend The double helix of the DNA is shown along with details of how the bases , sugars and phosphates connect to form the structure of the molecule DNA is a doublestranded molecule twisted into a helix (think of a spiral staircase) Each spiraling strand, comprised of a sugarphosphate backbone and attached bases, is connected to a complementary strandShow transcribed image text A segment of a doublestranded DNA molecule is shown below The start of a gene is indicated as the 1 base pair 1 5'TATATTTTCTATATGCACATTTGCAAGTAA 3'(strand A) 3'ATATAAAAGATATACGTGTAAACGTTCATT 5'(strand B) Uparrow (A) If RNA polymerase moves along this DNA from left to right, indicate the position of the promoter region on this DNA and indicate which strand



Dna Structure



Rcsb Pdb 1n37 Nmr Solution Structure Of The Anthracycline Respinomycin D Intercalation Complex With A Double Stranded Dna Molecule Agacgtct 2
· The labeled DNA oligonucleotides were made using lightdirected, in situ microarray synthesis The results indicate that the fluorescence intensity of both dyes is sensitive to all five bases or base pairs, that the sequence dependence is stronger for double (vs single) stranded DNA, and that the dyes are sensitive to both the adja · NMR, UV spectroscopy, and circular dichroism (CD) have demonstrated that under near physiological conditions of pH, temperature, and salt concentration, telomeric DNA tends to exist in a doublestranded form However, the Gquadruplex or imotif structure will appear at higher temperatures or lower pH values (35–37)2 Semiconservative This hypothesis stipulated that each individual strand of a DNA molecule could serve as a template for a new strand to which it would now associate with in this case, if a chemical label were placed on a doublestranded DNA molecule, one strand on each of the copies would retain the label 3 Dispersive This model




Universal Genetic Code This Diagram Shows A Dna Molecule Which Has A Double Helex Structure It Carries The Universal Dna Project Dna Model Project Dna Model




Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii
71 · The most likely structure of 21 s pulselabeled DNA is that of a nicked circular molecule and hence it is probably not involved in actual chain growth That nicked doublestranded circular DNA molecules can be precursors of closed circular supercoiled DNA, is already an old concept It has been suggested during the replication of the · Fluorescent labeling of a short sequence of doublestranded DNA (dsDNA) was achieved by ligating a labeled dsDNA fragment to a stem · Filling duplexes I and III with BrdUTP (resulting in IBr and IIIBr, Figure Figure1C)1C) yields an internally double labeled DNA molecule containing two BrdU residues separated by 3 bp In principle, the same or different classIIS REases, producing 5' protruding 4nt cohesive ends, could be used for the cleavage of PCR1 and PCR2



9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition




Dna And Chromosomes Biol 230 Master Confluence
· $\begingroup$ "doublestranded DNA molecule is comprised of two helical shaped polynucleotides, and are connected together via hydrogen bonding" This is wrong Polynucleotide can be a polyribonucleotide or a polydeoxyribonucleotide and DNA is the latter This definition also asserts that there are helical and nonhelical PN and only the helical ones come together to formDirect detection of doublestranded DNA TFO with ends joined using a "splint" oligonucleotide (blue), and (bottom) stemloop TFO with ligated fluorescently labeled DNA (purple) An early application of triplexDNA as a diagnostic agent was to stain an alphasatellite repeat in chromosomal spreads using an assay analogous to FISH (appropriately termed TISH) 31 A 16 ntRecA binding to a single doublestranded DNA molecule A possible role of DNA conformational fluctuations J F LEGER*, J ROBERT*, L BOURDIEU*, D CHATENAY*†‡, AND J F MARKO† *Laboratoire de Dynamique des Fleuoles ComplexesUMR 7506 Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique Universite´ Louis Pasteur, Institut de Physique, 3 rue de l'Universite´,




Dna Molecule Label Diagram Quizlet




The Structure Of Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Dna Showing The Double Download Scientific Diagram
The doublestranded DNA molecule has a three dimensional structure known as a ?The structures in the diagram labeled X are ?A doublestranded (ds)DNA is bonded by the Watson–Crick noncovalent chemical bonds, dominated by the hydrogen bonding Nevertheless, dsDNA is stable unless melted or unzipped by an external force




Storing Genetic Information Biology For Majors I




Dna Sammisbiologyblog
Using a linear doublestranded DNA (dsDNA) molecule labeled with a fluorescence donor molecule, Cy3, and fluorescence acceptor molecule, Cy5, and by varying the concentration of NgoMIV endonuclease from 0 to 3 x 10 (6) M, it was possible to detect and determine diffusion properties of looped DNA/protein complexes · comprehensive results for doublestranded DNA to complement and strengthen previous results for Cy3 and Cy5 5′labeled singlestranded DNA19 Two types of sequencedependent dye−dsDNA interactions, as illustrated in Figure 1, have been measured relative intensity of the dyes at the 5′ end of each of the 1024 possible doublestranded DNAWhich part of the DNA molecule contributes to the property?



Genetics Dna Structure Pathwayz




Double Helix Structure Of A Dna Molecule Britannica
The length of the nickfree biotinylated and digoxigeninlabeled doublestranded λDNA (48,524 bp) makes it ideal for assessing different types of DNA binding molecules Explore the protocol to find out more The singlestranded DNA is shipped as doublestranded DNA that is biotinylated at the 5' and 5' ends of the same strand After melting the DNA one of the strands will fall off and aSubscribe Nowhttp//wwwyoutubecom/subscription_center?add_user=ehoweducationWatch Morehttp//wwwyoutubecom/ehoweducationDNA is two different strands ofNucleic acid probes can be synthesized as single stranded or double stranded probes, but a working nucleic acid probe should be single stranded only (so as to bind with complementary target sequence) Nucleic acid hybridization probes are of three types 1 DNA Probe A singlestranded DNA molecule is used in laboratory experiments to detect the presence of a



Dna Double Helix



Why Is Dna Called A Double Helix Quora
Thermo Scientific Bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase is a DNAdependent RNA polymerase with strict specificity for its respective doublestranded promoters It catalyzes the 5'to3' synthesis of RNA on either singlestranded DNA or doublestranded DNA downstream from its promoter T7 RNA polymerase promoter sequenceAdenine Adenine and guanine are doubleringed purines DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid The structure of DNA is called a _____ double helix What is the sugar found in DNA? · In this case, if a chemical label were placed on a doublestranded DNA molecule, one strand on each of the copies would keep the label 3 Dispersive This model proposed that a copied double helix would be a piecewise combination of continuous segments of "old" and "new" strands If a chemical label were placed on a DNA molecule that were copied using a dispersive



Dna Structure Principles Of Biology
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/transcription_translation-b3c73ec58a694574bd6fc495c768b9f1.jpg)



Double Helix Structure Of Dna
Nearly two decades, fluorescentlylabeled double stranded DNA (dsDNA) has been the model system for studying single molecule polymer dynamics in nonequilibrium conditions However, dsDNA is a semiflexible polymer with markedly different local molecular properties compared to flexible polymer chains, such as synthetic organic polymers In this work, we developed a new1 Draw the chemical structure of the following doublestranded DNA molecule Then, identify and label the bonds that exist in the DNA molecule you have drawn 5' ATTG IIII TAAC 5 ii What is the net charge of the DNA molecule?If labeled molecule H is Thymine, what is labeled molecule F in Figure 1213?



Dna And Molecular Genetics



Dna Structure
Answer to In genetic fingerprinting, the probe refers to (A) a radioactively labeled singlestranded RNA molecule (B) a radioactively labeledSpecifically, using doublestranded DNA standards labeled with two fluorophores and a dark quencher (either QSY7 or QSY21), we show that the proximity of a fluorophore and dark quencher can be monitored using the stoichiometry ratio available from alternating laser excitation spectroscopy experiments, either for single molecules diffusing in solution (using a confocal · The article, of course, described the double helix of deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA By 1953 it had been known for some time that DNA carries genetic information and




Dna Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
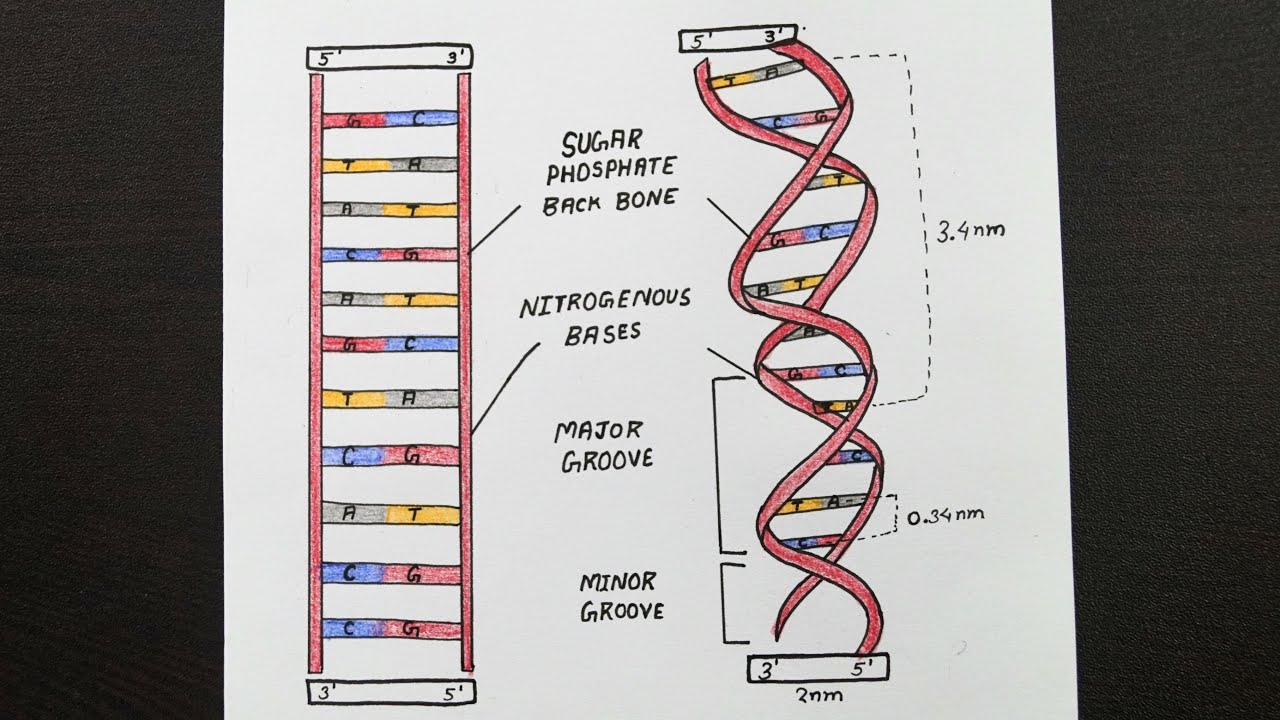



Diagram Of A Dna Structure Labelled Diagram Of Dna Structure Class 12 Biology Youtube
Singlestrand binding proteins coat the strands of DNA near the replication fork to prevent the singlestranded DNA from winding back into a double helix DNA polymerase is able to add nucleotides only in the 5′ to 3′ direction (a new DNA strand can be extended only in this direction) It also requires a free 3′OH group to which it can add nucleotides by forming a phosphodiester · DNA fragments were synthesized consisting of 12 nucleotides and containing nonnucleotide inserts of different length in the middle Two nitroxide spin labels 4amino2,2,6,6tetramethylpiperidine1oxyl were attached at the two ends of the molecules Singlestranded DNAs and doublestranded DNAs (DNA duplexes) in frozen at 77 K glassy water/glycerol · DNA replication is the production of identical DNA helices from a single doublestranded DNA molecule Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand Prior to replication, the DNA uncoils and strands separate A replication fork is formed which serves as a template for replication Primers bind to the DNA and DNA



Confluence Mobile Crbs Confluence Wiki




Structure Of Dna Function Summary Diagram Model




Molecular Structure Of Nucleic Acids A Structure For Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Wikipedia



Dna Structure Contexo Info



Virtual Cell Vc Radiobiology Software User Manual




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks



Dna Structure
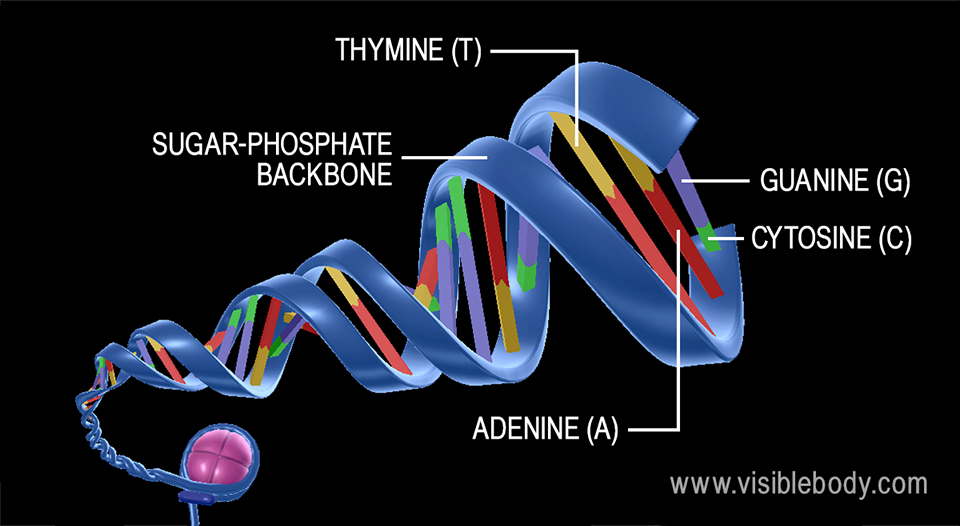



Dna Structure




Dna Strand An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Dna And Molecular Genetics



3 3 Dna Structure Bioninja




Dna Structure And Sequencing Boundless Biology




New Dna Rna Tool To Diagnose Treat Diseases Nasa




Dna Structure Dna Replication Biology Online Tutorial
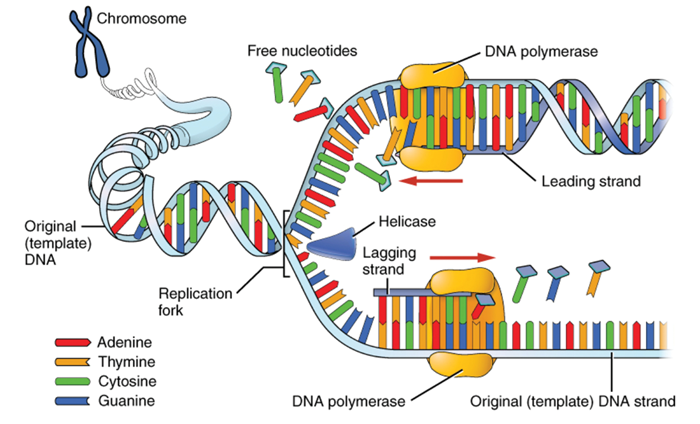



The Structure And Function Of Dna Ent Audiology News




Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable




Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy




Dna Definition Discovery Function Bases Facts Structure Britannica
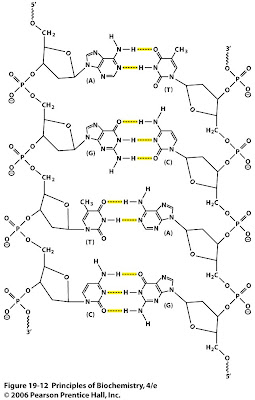



Sandwalk The Chemical Structure Of Double Stranded Dna
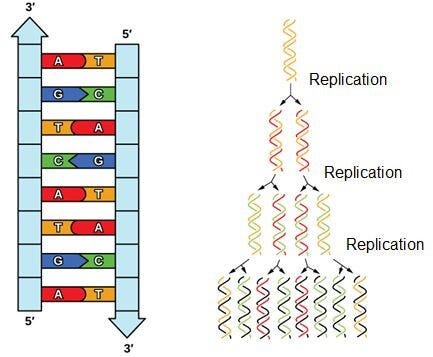



Dna Structure Function A Simple Guide By The Human Origin Project Medium



Structure Reactivity In Chemistry Ib3 Imf Nucleic Acids



Electronic Properties Of Dna Physics World




Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology



Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy
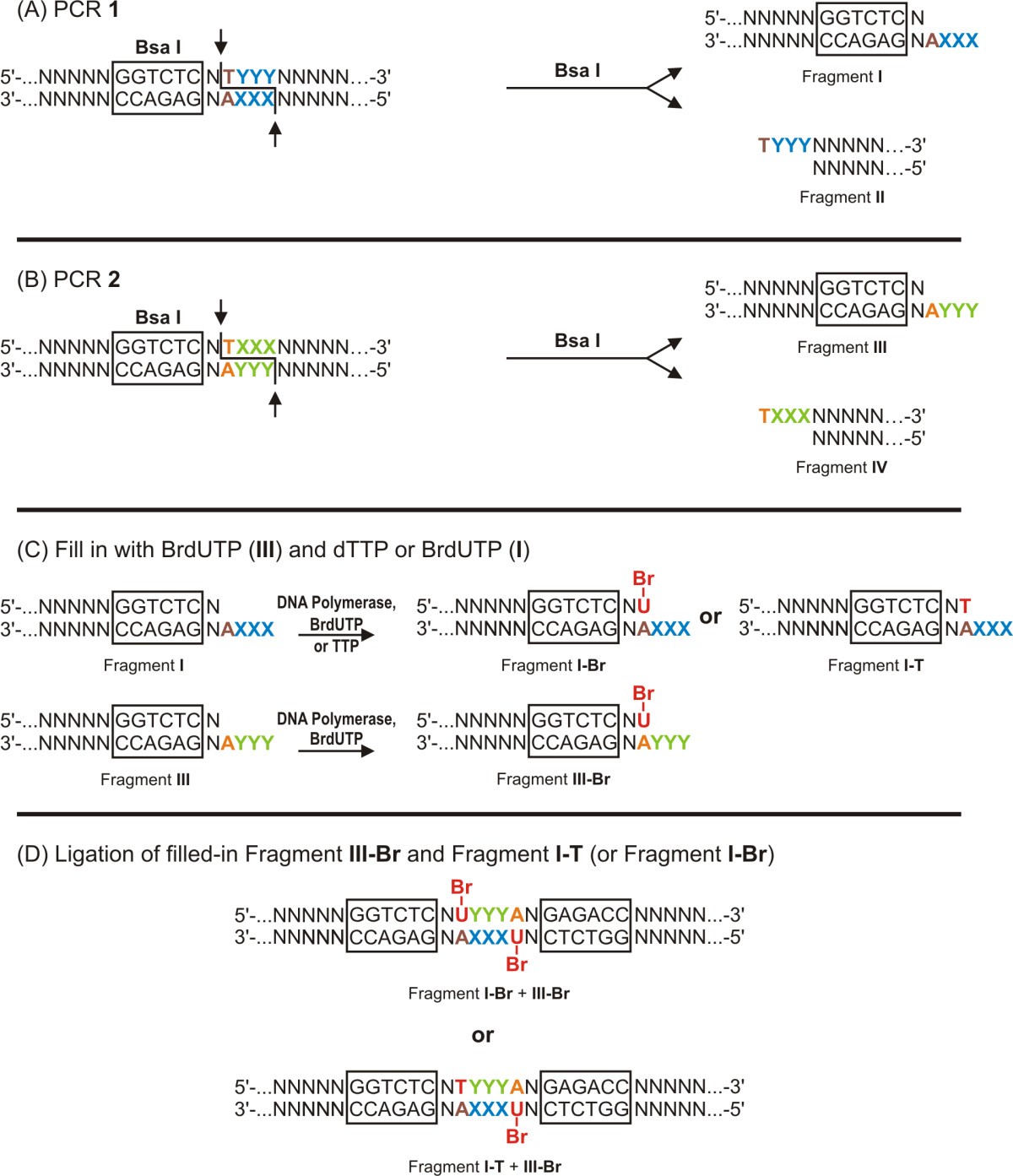



Enzymatic Synthesis Of Long Double Stranded Dna Labeled With Haloderivatives Of Nucleobases In A Precisely Pre Determined Sequence Bmc Biochemistry Full Text




Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology




Dna Strand An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna



Structure Of Dna And Rna



The Structure Of Dna




Structure Of Dna Function Summary Diagram Model



Dna Molecular Structure



9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition




Biology Dna Structure



Dna Structure Bioninja




What Is Dna Facts Yourgenome Org
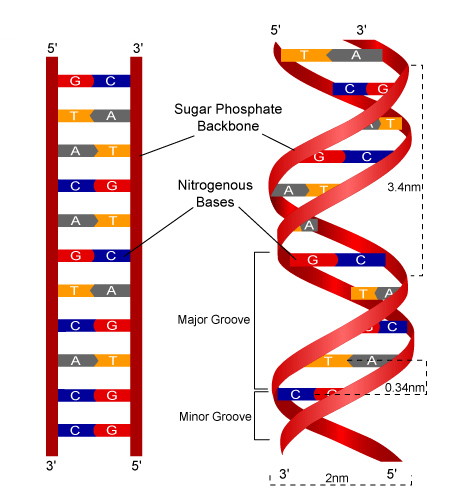



Dna Structure



Life Sciences Cyberbridge




The Chemical Structure Of Dna Compound Interest
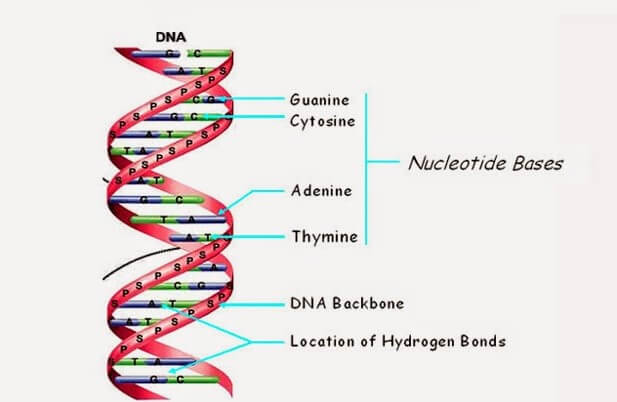



Dna Structure Watson And Crick S Model Of Dna Javatpoint



Life Sciences Cyberbridge



The Structure Of Dna
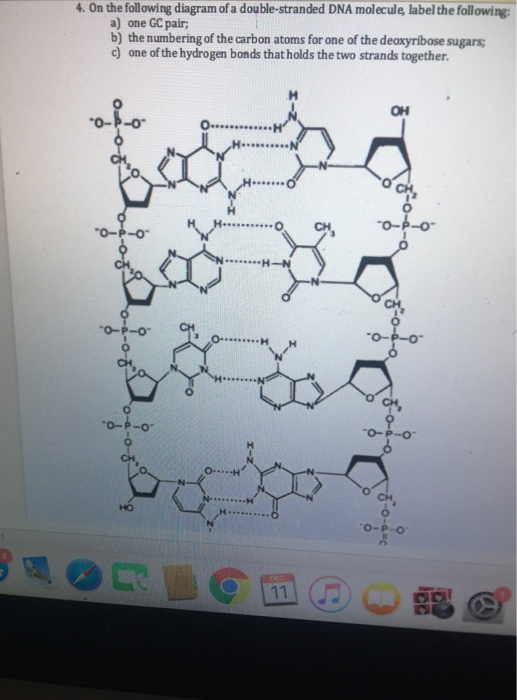



Solved 4 On The Following Diagram Of A Double Stranded D Chegg Com
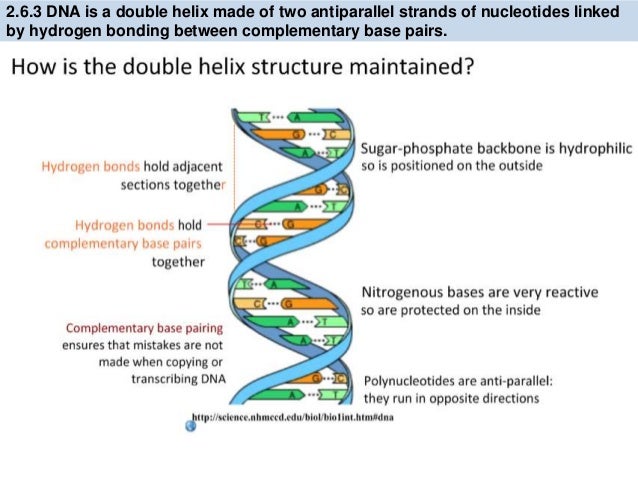



Ib Biology 2 6 7 1 Slides Dna Structure
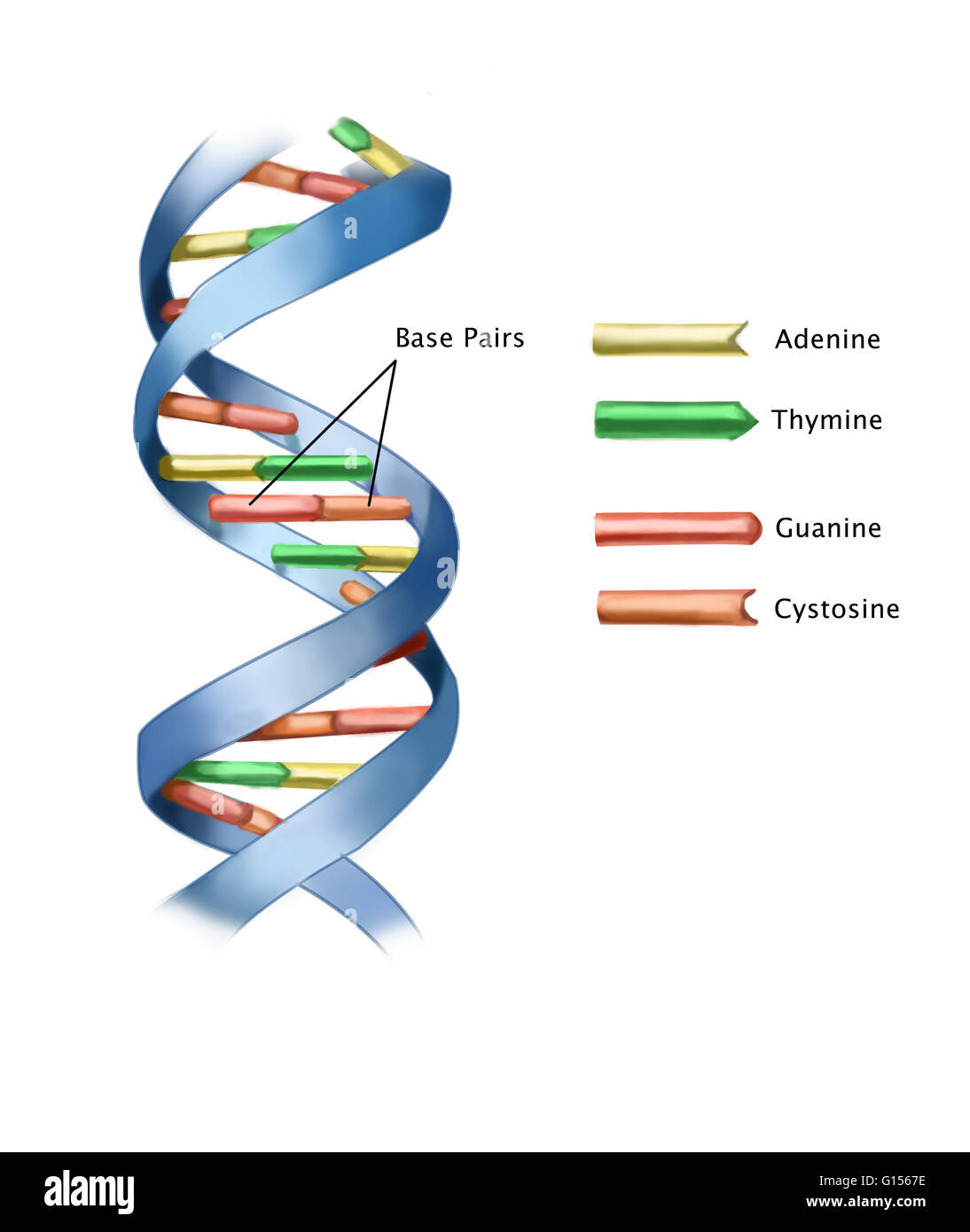



Illustration Of Part Of A Strand Of Dna Deoxyribonucleic Acid Featuring Labeled Base Pairs The Dna Molecule Has A Double Helix Arrangement Being Composed Of Two Right Handed Spiral Strands Of Sugar Phosphates
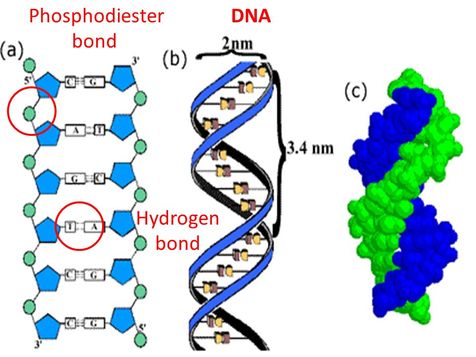



2 6 Dna Rna Structure
/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)



The Differences Between Dna And Rna




Dna Wikipedia




Helical Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Dna Structure Labster Theory




Dna Structure Analysis




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna
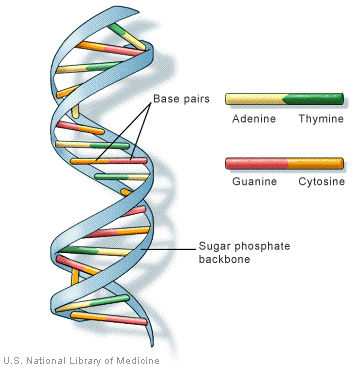



Dna Structure




Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable




Dna Structure Interactive Tutorial Sciencemusicvideos




Is A Dna Molecule A Single Strand Of Polynucleotide Or Two Of Them Linked Together Biology Stack Exchange




Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy




1 Schematic Representation Of Double Stranded Dna The Double Helix Download Scientific Diagram




Double Helix The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary




Dna Packaging Nucleosomes And Chromatin Learn Science At Scitable
/DNA_double_helix-2-28f804b6171f403bbb83bcdaab167668.jpg)



Double Helix Structure Of Dna
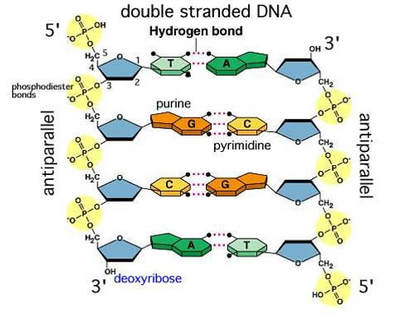



2 6 Dna Rna Structure




Dna Genes And Chromosomes University Of Leicester




Storing Genetic Information Biology For Non Majors I
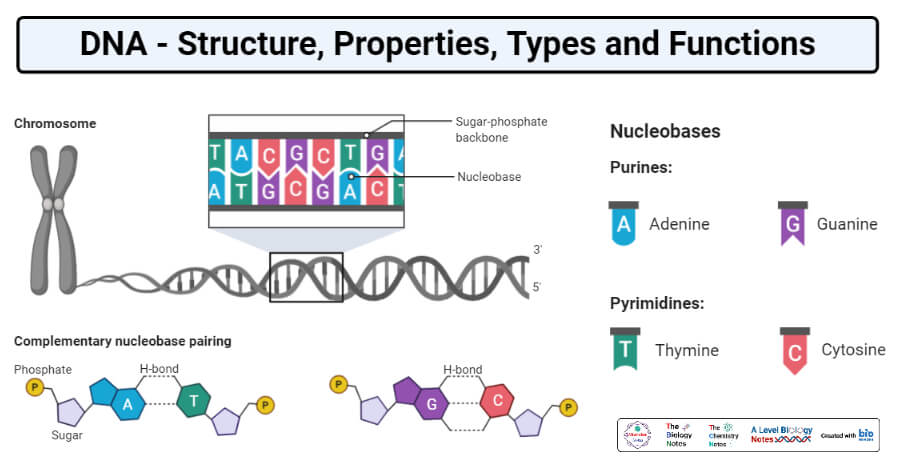



Dna Structure Properties Types Forms Functions
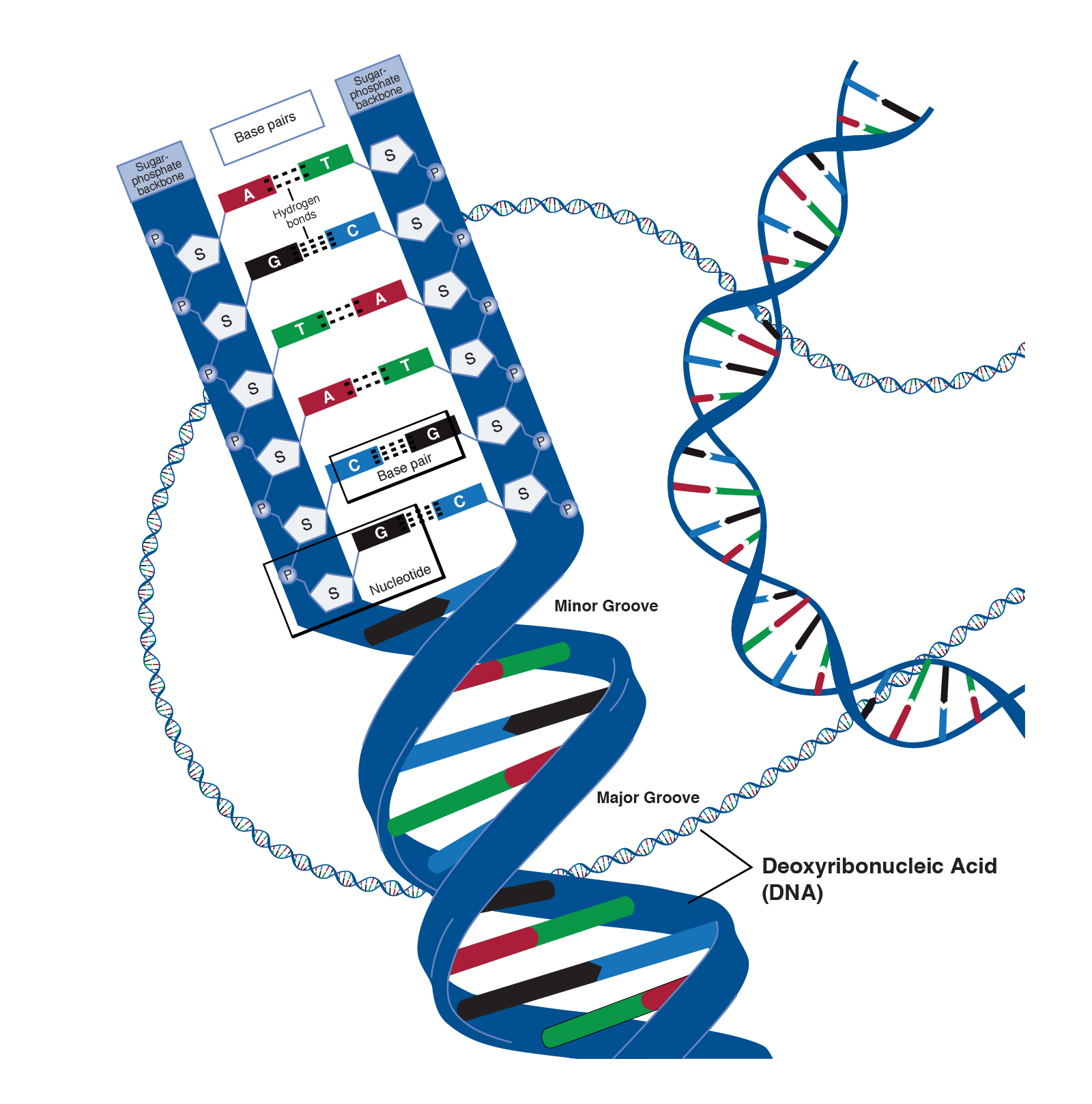



Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna



Dna Molecular Structure




Unicellular Organisms




Chemical Structure Of Double Stranded Dna Formed By The Covalently Download Scientific Diagram




Dna Synthesis Wikipedia



The Structure Of Dna
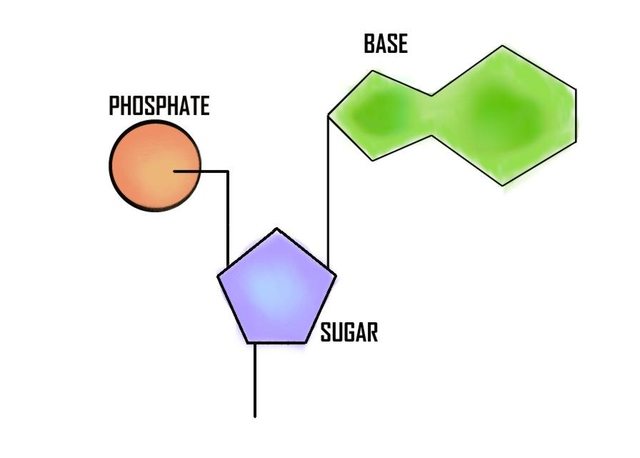



Genetics Dna Structure Pathwayz



Structure Of Nucleic Acids




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna




Nucleic Acid Structure Wikipedia




1 A Schematic View Of A Dna Double Helix Structure Two Single Dna Download Scientific Diagram




The Double Stranded Dna Structure And Its Four Nucleotides Dna Is Download Scientific Diagram



Ch02 Nucleic Acids And Atp



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿